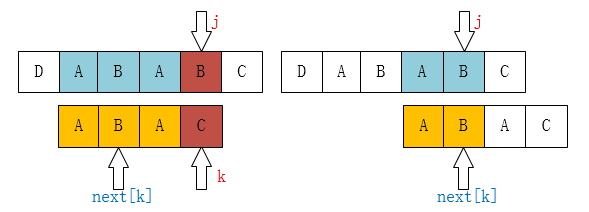
Algorithm__并查集
Algorithm__滑动窗口
滑动窗口主要用来处理连续问题。比如题目求解“连续子串 xxxx”,“连续子数组 xxxx”,就应该可以想到滑动窗口。能不能解决另说,但是这种敏感性还是要有的。
从类型上说主要有:
- 固定窗口大小
- 窗口大小不固定,求解最大的满足条件的窗口
- 窗口大小不固定,求解最小的满足条件的窗口(上面的 209 题就属于这种)
后面两种我们统称为可变窗口。当然不管是哪种类型基本的思路都是一样的,不一样的仅仅是代码细节。
固定窗口大小
对于固定窗口,我们只需要固定初始化左右指针 l 和 r,分别表示的窗口的左右顶点,并且保证:
- l 初始化为 0
- 初始化 r,使得 r - l + 1 等于窗口大小
- 同时移动 l 和 r
- 判断窗口内的连续元素是否满足题目限定的条件
- 4.1 如果满足,再判断是否需要更新最优解,如果需要则更新最优解
- 4.2 如果不满足,则继续。
可变窗口大小
对于可变窗口,我们同样固定初始化左右指针 l 和 r,分别表示的窗口的左右顶点。后面有所不同,我们需要保证:
- l 和 r 都初始化为 0
- r 指针移动一步
- 判断窗口内的连续元素是否满足题目限定的条件
- 3.1 如果满足,再判断是否需要更新最优解,如果需要则更新最优解。并尝试通过移动 l 指针缩小窗口大小。循环执行 3.1
- 3.2 如果不满足,则继续。
形象地来看的话,就是 r 指针不停向右移动,l 指针仅仅在窗口满足条件之后才会移动,起到窗口收缩的效果。
1 | class Solution { |
1 | class Solution { |
1 | class Solution { |
Algorithm__堆和队列
Algorithm__树
树的遍历——颜色标记法
我们知道垃圾回收算法中,有一种算法叫三色标记法。 即:
- 用白色表示尚未访问
- 灰色表示尚未完全访问子节点
- 黑色表示子节点全部访问
那么我们可以模仿其思想,使用双色标记法来统一三种遍历。
其核心思想如下:
- 使用颜色标记节点的状态,新节点为白色,已访问的节点为灰色。
- 如果遇到的节点为白色,则将其标记为灰色,然后将其右子节点、自身、左子节点依次入栈。
- 如果遇到的节点为灰色,则将节点的值输出。
1 | class Solution |
Algorithm__链表
链表
链表的注意点
- 出现了环,导致了死循环
- 分不清楚边界,导致边界出错
- 搞不清递归
环
- 判断是否有环,以及环的位置————快慢指针算法
边界
- 当题目中的头节点需要进行操作时,可能会被移除时,要考虑使用虚拟节点,也就是头节点。这样操作就会避免对第一个节点的讨论
前后序
相较于树,在链表中只有一个后续指针,只有前序和后序,没有中序遍历。
如果是前序遍历,那么你可以想象前面的链表都处理好了,怎么处理的不用管。相应地如果是后序遍历,那么你可以想象后面的链表都处理好了,怎么处理的不用管。
- e.g.前序遍历
1 | def dfs(head,pre): |
一些技巧
头结点————虚拟结点
头结点不需要参与运算,不需要特殊判断
快慢指针
判断链表是否有环以及环的入口。
1 | public class Solution { |
leetcode题目
1 | class Solution { |
1 | class Solution { |
此题最为巧妙的是运用了头指针,这样可以减少对第一个元素的讨论。
1 | //迭代 |
1 | /** |
1 | //还是使用左右指针 |
1 | //常规方法是可以想到的,这道题的递归是不容易想到的 |
1 | class Solution { |
1 | /* 知识点1:归并排序的整体思想 |
1 | //迭代 |
Algorithm__回溯算法
回溯
回溯法思路的简单描述是:把问题的解空间转化成了图或者树的结构表示,然后使用深度优先搜索策略进行遍历,遍历的过程中记录和寻找所有可行解或者最优解。
回溯法的基本行为是搜索,搜索过程使用剪枝函数来为了避免无效的搜索。剪枝函数包括两类:1. 使用约束函数,剪去不满足约束条件的路径;2.使用限界函数,剪去不能得到最优解的路径。
回溯法实现————递归和迭代
1 | /* |
1 | /* |
1 | //全排列的两道题目和组合总和的两道题目本质上是差不多的,在存在重复数字的时候,这里采用的的方法是: |
1 | class Solution { |
1 | class Solution { |
想在子集1的基础上进行修改,但是去重实现的不好,暂时不知道怎么处理
1 | /* |
Algorithm_字符匹配算法
KMP算法
主要的关键点在于NEXT数组————最长公共前后缀
寻找前后缀的方法:
- 找前缀时,要找除了最后一个字符的所有子串
- 找后缀时,要找除了第一个字符的所有子串
1 | void Getnext(int next[],String t) |
当P[k] == P[j]时,
有next[j+1] == next[j] + 1
毕设笔记
SLAM(同步定位与建图)
SLAM研究体系分类
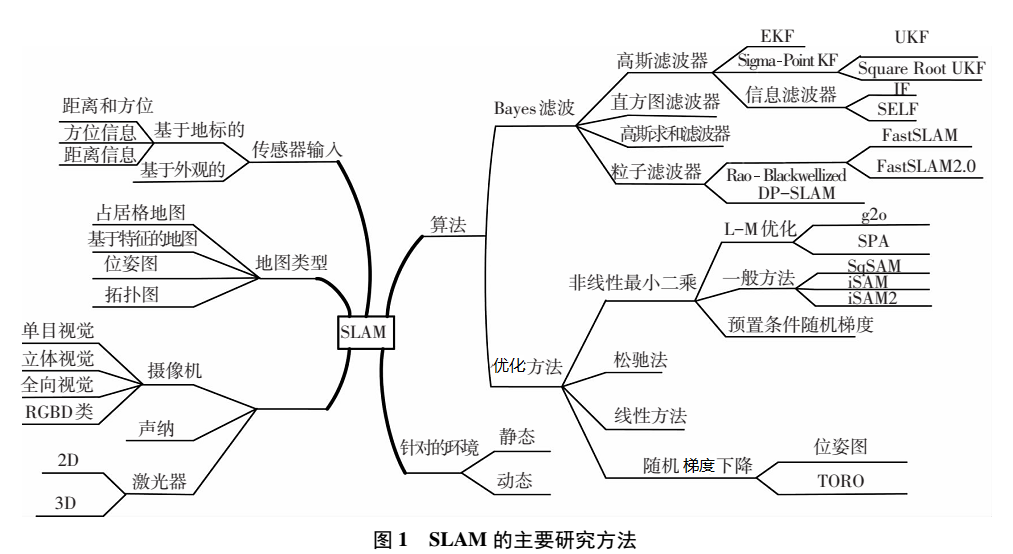
SLAM通常包括如下几个部分,特征提取,数据关联,状态估计,状态更新以及特征更新等。
SLAM的一般过程
SLAM的核心是EKF。EKF用于结合上述信息估计机器人准确位置。上述选取的特征一般称作地标。EKF将持续不断的对上述机器人位置和周围环境中地标位置进行估计。
ekf,扩展卡尔曼滤波简称,太偏向物理方面了
特征提取
- slam的第一步需要通过测距单元获取机器人周围环境的信息。
- 具体的方式可以通过激光测距,或者在仿真的时候直接给出
- 机器人自身运动模型:机器人自身位置数据通过对机器人轮胎运行圈数的估计可以得到机器人自身位置的一个估计,其可以被看作EKF的初始估计数据
- 需要注意需要保证机器人自身位置数据与测距单元数据的同步性。为了保证其同步性,一般采用插值的方法对数据进行前处理
- 特征(即是地标)
- 地标是环境中易于观测和区分的特征
- 地标应该可以从不同的位置和角度观察得到
- 地标应该是独一无二的,从而可以很容易的将底边从其他物体中分辨出来
- 地标是环境中易于观测和区分的特征
数据关联
是将不同时刻位置传感器提取到的地标信息进行关联的过程,也成为重观察过程。
- 此处在仿真的时候,可以选择依赖或者不依赖先验知识,直接从图像序列中检测到运动目标,然后进行目标识别
路径规划
所谓机器人的最优路径规划问题就是根据某个或某些优化准则,如工作代价最小,行走路径最短,行走时间最短等准则,在其工作空间中找到一条从起始点到目标点的能避开障碍物的最优路径。
需要解决的问题分为下面三点:
- 始于初始点止于目标点
- 避开障碍
- 尽可能优化路径
常见的路径规划
基于采样的方法、基于节点的方法、基于数学模型的算法、基于生物启发式的算法、和多融合算法。此处重点关注的是基于节点的方法。————可以采用学过的Dijkstra法、A*法
A*法的介绍:也称为栅格法。
通过下面这个函数来计算每个节点的优先级。
$$
f(n)=g(n)+h(n)
$$
其中:
- f(n)是节点n的综合优先级。当我们选择下一个要遍历的节点时,我们总会选取综合优先级最高(值最小)的节点。
- g(n) 是节点n距离起点的代价。
- h(n)是节点n距离终点的预计代价,这也就是A*算法的启发函数。关于启发函数我们在下面详细讲解。
A*算法在运算过程中,每次从优先队列中选取f(n)值最小(优先级最高)的节点作为下一个待遍历的节点。
A*算法使用两个集合来表示待遍历的节点,与已经遍历过的节点,这通常称之为
open_set和close_set。```
- 初始化open_set和close_set;
- 将起点加入open_set中,并设置优先级为0(优先级最高);
- 如果open_set不为空,则从open_set中选取优先级最高的节点n:
- 如果节点n为终点,则:
- 从终点开始逐步追踪parent节点,一直达到起点;
- 返回找到的结果路径,算法结束;
- 如果节点n不是终点,则:
- 将节点n从open_set中删除,并加入close_set中;
- 遍历节点n所有的邻近节点:
- 如果邻近节点m在close_set中,则:
- 跳过,选取下一个邻近节点
- 如果邻近节点m也不在open_set中,则:
- 设置节点m的parent为节点n
- 计算节点m的优先级
- 将节点m加入open_set中
function heuristic(node) =
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
5. 启发函数
- Dijkstra算法就是启发函数h(n)=0时的A*算法
- 如果h(n)始终小于等于节点n到终点的代价,则A*算法保证一定能够找到最短路径。但是当h(n)的值越小,算法将遍历越多的节点,也就导致算法越慢。
- 如果h(n)完全等于节点n到终点的代价,则A*算法将找到最佳路径,并且速度很快。
- 如果h(n)的值比节点n到终点的代价要大,则A*算法不能保证找到最短路径,不过此时会很快。
在一些情况,我们可能未必需要最短路径,而是希望能够尽快找到一个路径即可
这里我们的启发函数采用欧几里得距离:两个节点之间的直线距离
dx = abs(node.x - goal.x)
dy = abs(node.y - goal.y)
return D * sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy)oscillation_costs_ //振荡代价函数,一旦速度发生振荡,直接丢弃速度样本
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
A\*算法的变种:ARA*、D*、Field D*
## A*算法的优化
### 估值函数的改进h(n)

### 估值函数中引入惩罚函数
## 基于DWA的局部路径规划算法
当移动机器人遇到动态的障碍物时,需要针对突然出现的物体有自主避障的能力--因此需要局部路径规划
### DWA介绍
[参考文章](https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_37835423/article/details/89683302)
————动态窗口法
其算法过程主要分为仿真获取机器人的运动轨迹、对轨迹进行评价选择最优轨迹两个主要过程,动态窗口表达的是仿真的运动轨迹数量有限,主要是因为机器人在较短的控制周期内只能达到一定的速度。
#### 获取移动机器人速度样本
对移动机器人的速度空间(v,w)[v表示的是线速度,w表示的是角速度]进行采用,通过建模对采样的速度进行轨迹预测,通过评价函数对预估的轨迹进行评价
#### 生成运动轨迹
根据速度样本确定运动轨迹,是简单运行学知识,主要注意的是用的仿真时间产生的样本还是仿真周期产生的样本。
#### 针对轨迹进行评价并选取最优轨迹
obstacle_costs_ //障碍物代价函数,当轨迹进入障碍物区,直接丢弃当前轨迹样本
goal_costs_ //目标代价函数,优先选择距离局部目标点近的轨迹
path_costs_ //路径代价函数,优先选择贴近全局路径的轨迹
```
- 通过仿真轨迹将机器人轮廓映射到全局坐标系下,并对轮廓边上的代价值进行分析,选择最大的代价值作为障碍物代价,从而确定机器人是否会撞到障碍物
- 首先根据全局路径与局部代价地图的边界确定局部目标点,然后依据局部目标点生成栅格地图,每个栅格处的值代表当前栅格到目标点的距离,对于障碍物栅格,直接置为到目标点的距离无穷远。最后再根据轨迹末端点处栅格的位置,直接通过索引在地图中获取该位置距目标点的距离,作为距目标点的代价。因此,目标代价函数的主要任务是生成栅格地图。
- 该代价函数的实现原理与目标代价函数类似,只是该函数是以局部路径上的所有点作为起点向外膨胀来构建栅格地图,并且是以仿真轨迹上的所有点的距离值的和的平均值作为轨迹的代价值。